I examined this in a bit more detail and just applied common sense to nail the lies that are being told to the public , on this .
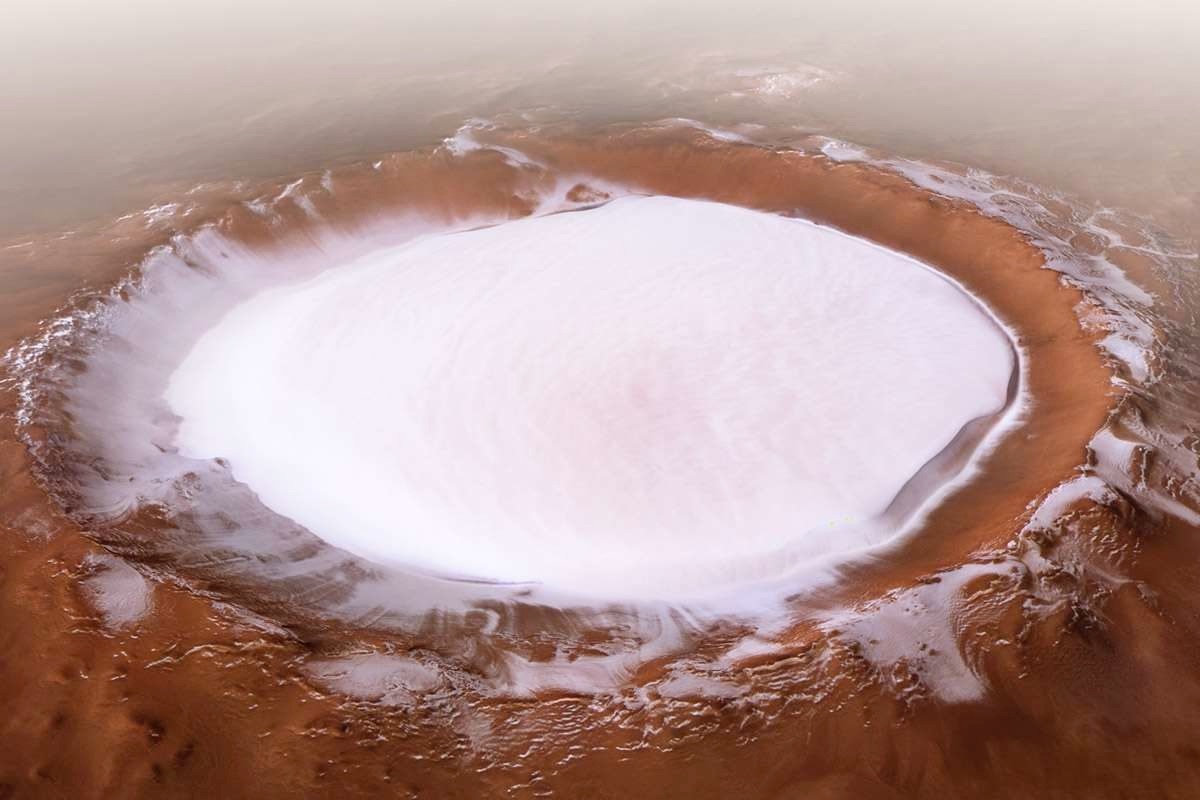
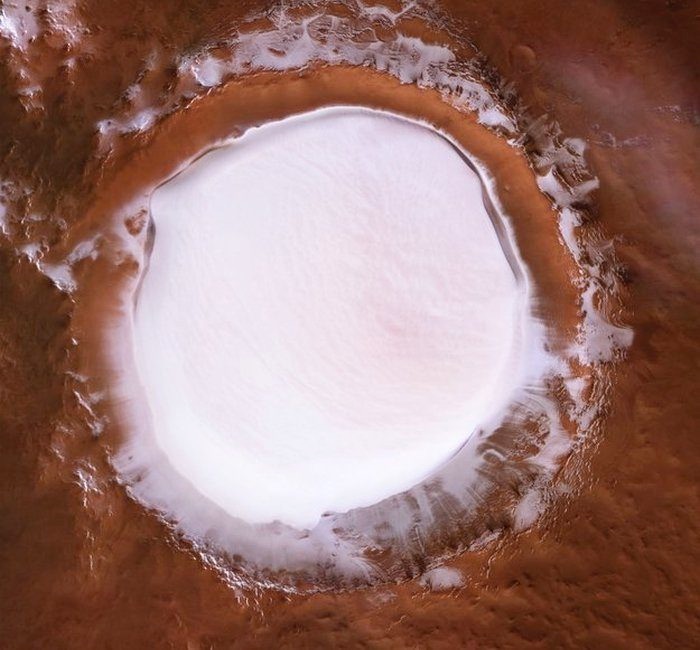
Notice how scant the Martian atmosphere is , so there is no question of it containing the huge amount of moisture required to precipitate out a 1.2 mile thick layer of snow at the Poles each year . Even the moisture rich atmosphere of Earth does not precipitate that much snow a year , even in frigid Antarctic (comparable to Martian cold) .
Secondly , the average temperature ACROSS the Martian surface is -63 degrees centigrade (-82 degrees Fahrenheit) . That is so cold that if the Martian atmosphere was thick enough and had adequate moisture , then the deposition of snow would happen ALL OVER the planet's surface (!!) , NOT just restricted to a 67 mile area at it's North Pole ! That proves the BIG lie being told to us , especially because they themselves insist dry ice - frozen CO2 , is only a meter deep , the rest of the Martial North Polar ice cap being frozen H20 :))
Mars’ Atmosphere
Posted on February 1, 2017 by Matt Williams
** Mars has a very thin atmosphere which is composed of 96% carbon dioxide, 1.93% argon and 1.89% nitrogen,
along with traces of oxygen and water.** The atmosphere is quite dusty, containing particulates that measure 1.5 micrometers in diameter, which is what gives the Martian sky its tawny color when seen from the surface. Mars’ atmospheric pressure ranges from 0.4 to 0.87 kPa, which is the equivalent of about 1% of Earth’s at sea level.
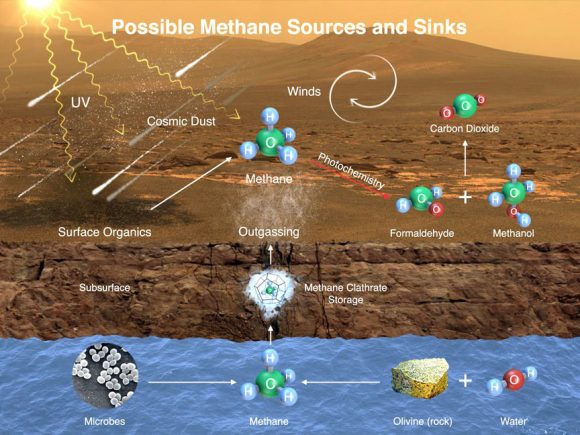
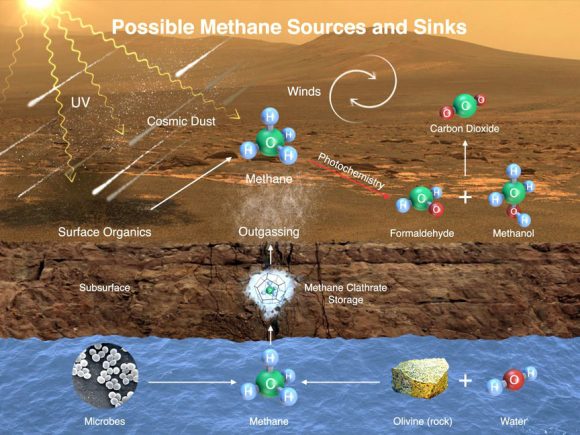 * This
* This
image illustrates possible ways methane might get into Mars’ atmosphere
and also be removed from it. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/SAM-GSFC/Univ. of
Michigan*
Because of this thin atmosphere, and its greater distance from the Sun, the surface temperature of Mars is much colder than what we experience here on Earth. The planet’s average temperature is -63 °C (-82 °F), with a low of -143 °C (-226 °F) during the winter at the poles, and a high of 35 °C (95 °F) during summer and midday at the equator.
Due to the extreme lows in temperature at the poles, 25-30% of the carbon dioxide in the atmosphere freezes and becomes dry ice that is deposited on the surface. While the polar ice caps are predominantly water, the Martian North Pole has a layer of dry ice measuring one meter
thick in winter, while the South Pole is covered by a permanent layer that is eight meters deep.
Trace amounts of methane and ammonia have also been detected in the Martian atmosphere. In the case of the former, it has an estimated concentration of about 30 parts per billion (ppb), though the Curiosity rover detected a “tenfold spike”
on December 16th, 2014. This detection was likely localized, and the source remains a mystery. Similarly, the source of ammonia is unclear, though volcanic activity has been suggested as a possibility.
Meteorological Phenomena:
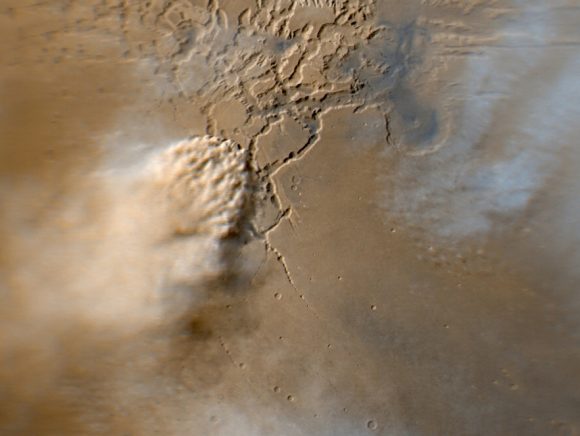
Mars is also famous for its intense dust storms, which can range from
small tornadoes to planet-wide phenomena. Instances of the latter coincide with dust being blown into the atmosphere, causing it to be heated up from the Sun. The warmer dust-filled air rises and the winds get stronger, creating storms that can measure up to thousands of kilometers in width and last for months at a time. When they get this large, they can actually block most of the surface from view.
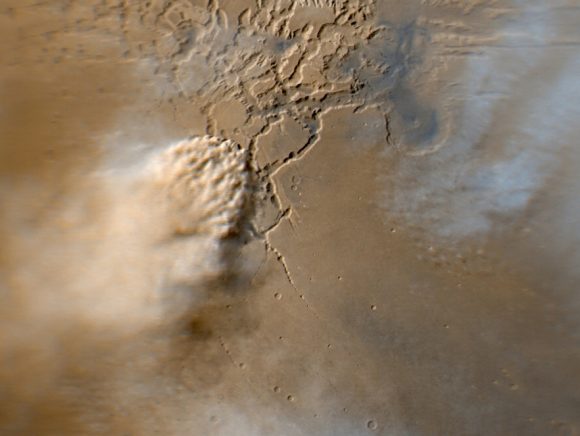 Image capturing an active dust storm on Mars. Image credits: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS
Image capturing an active dust storm on Mars. Image credits: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS
Due
to its thin atmosphere, low temperatures and lack of a magnetosphere, liquid precipitation (i.e. rain) does not take place on Mars. Basically,
solar radiation would cause any liquid water in the atmosphere to disassociate into hydrogen and oxygen. And because of the cold and thin atmosphere, there is simply not enough liquid water on the surface to maintain a water cycle.
Occasionally, however, thin clouds do form in the atmosphere and precipitation falls in the form of snow. This consists primarily of carbon dioxide snow ,
which has been observed in the polar regions. However, small traces of frozen clouds carrying water have also been observed in Mars’ upper atmosphere in the past, producing snow that is restricted to high altitudes.
One such instance was observed on September 29th, 2008, when the Phoenix lander
took pictures of snow falling from clouds that were 4 km (2.5 mi) above
its landing site near the Heimdal Crater. However, data collected from the lander indicated that the precipitation vaporized before it could reach the ground.
···
On Monday, December 24, 2018, 2:09:43 PM GMT+5:30, sidhartha bahadur [email protected] [ALLPLANETS-HOLLOW] [email protected] wrote:
Soretna , Dean , your observations are spot on - these images seem to have been very cleverly morphed , as usual .
First of all , precipitation in Mars bone dry & flimsy atmosphere , is woefully inadequate to create an ice-sheet 1.2 miles thick , every year !
I was also thinking , judging by relative sizes of Earth & Mars , that if the North Polar opening (being called a "crater" to mislead people) of Mars is 67 miles across , then the Polar opening on Earth could well be about 90 miles across , as many explorers have speculated .
Regards
On Sunday, December 23, 2018, 8:38:17 AM GMT+5:30, [email protected] [ALLPLANETS-HOLLOW] [email protected] wrote:
Soretna,
How can they say such things? 1.2 miles deep of ice at the North Pole crater, and 67 miles across? Their own images show (third image down) that the ice melts every summer.
http://www.holloworbs.com/real_mars.htm
How does 1.2 miles of ice build up every winter. That's pretty good for a planet with 2% of the Earth's atmosphere. How much moisture does 2% of the Earth's atmosphere deposit into a crater at the North Pole every winter, seeing how the planet doesn't even have one ocean?
There are no brillant deductions on my part, I have just eyeballed their own images. Don't the young people who study astrophysics at the university even look at the pictures?
NASA just says any old thing it wants to.
Where is Walter Cronkite?
And how come Hoagland doesn't jump all over these statements? And how come Hoagland doesn't comment on all the images of constructions, like that Bridge on Mars video?
Any trumphed up two-bit war in Europe with Russia over the Ukraine, and the western democracies (misnomer) would probably clamp down and absolutely censure the internet.
I'm getting scared.
Dean