List members , Venus is just so similar to Earth - it even has active volcanoes and it's very own "ring of fire" . The more one finds out about Venus , the more it helps justify it's epithet as "Earth's twin" :-
Venus may have enough active volcanoes to form its own 'ring of fire', new study finds
In proving that Venus is geographically active, scientists are looking to understand why Earth and Venus evolved so differently despite being so similar.
FP Trending Jul 27, 2020 09:00:46 IST
Venus, often known as Earth's twin, is considered to be an unusual planet for its circular orbit and its thick cloudy atmosphere. The presence of numerous volcanoes on the planet was a known fact but these were touted to have been dormant for ages.
But a recent study has revealed that some of these activities might be not as ancient as we thought. They could even be occurring in current times.
Researchers have identified 37 volcanic structures on Venus that appear to be recently active – and probably still are today – painting the picture of a geologically dynamic planet and not a dormant world as long thought.
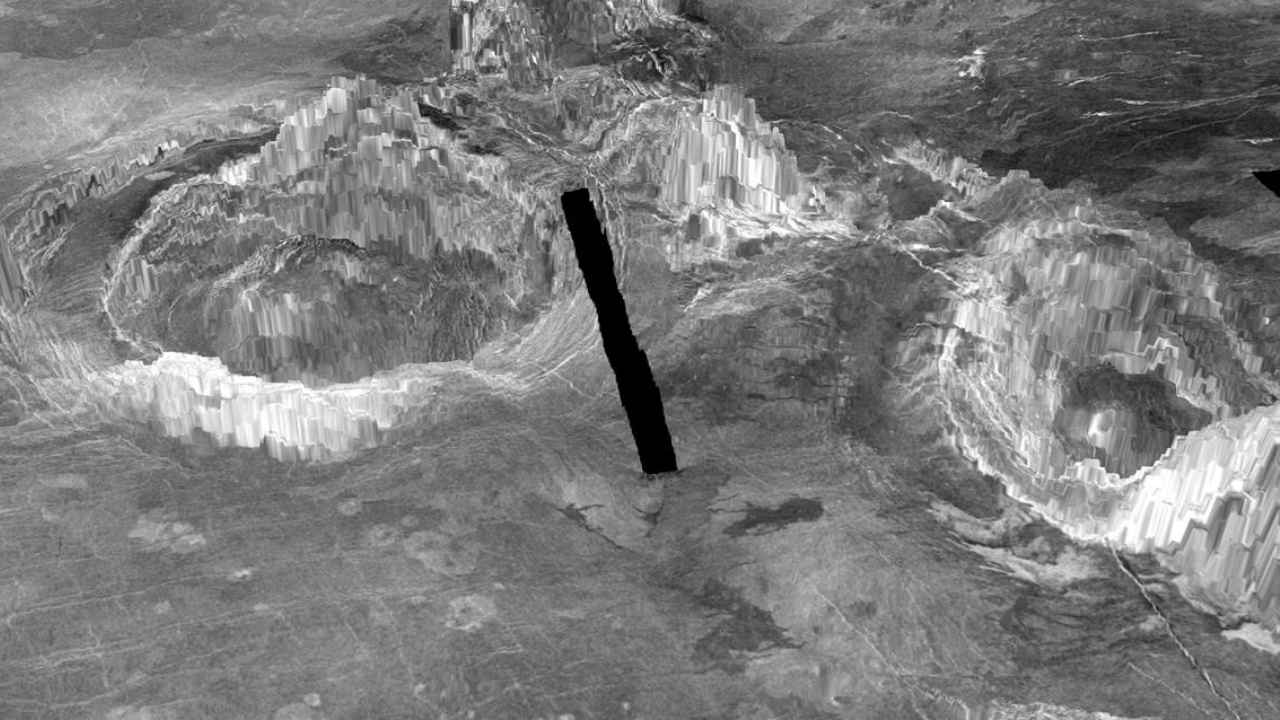
Two ring-like structures called coronae, which are formed when hot material from deep inside the planet rises through the mantle and erupts through the crust. These are two such structures on the surface of Venus in a 3-D rendition released on 20 July 2020. Image credit: Laurent Montesi/University of Maryland via Reuters
Scientists are using crown-like structures found on Venus to determine whether it is, like Earth, a volcanically-active planet.
On Earth, the 'Ring of fire' is a region in the basin of Pacific Ocean that is known to be seismically active – the most earthquake-prone region anywhere on the planet. Early research suggests that the extremely hot planet might have its own 'ring of fire', but the factors contributing to its presence on Venus might be different from Earth.
According to the study, multiple structures called coronae can be seen on the surface of the hot planet, gaining its name from the "crown-like" shape they leave behind on the surface. These are somewhat formed like the volcanoes on Earth - with plumes of hot magma coming out from Venus' core up to the crust. However, these are huge in comparison to earthly volcanoes, with diameters larger than 299.3 kilometre.
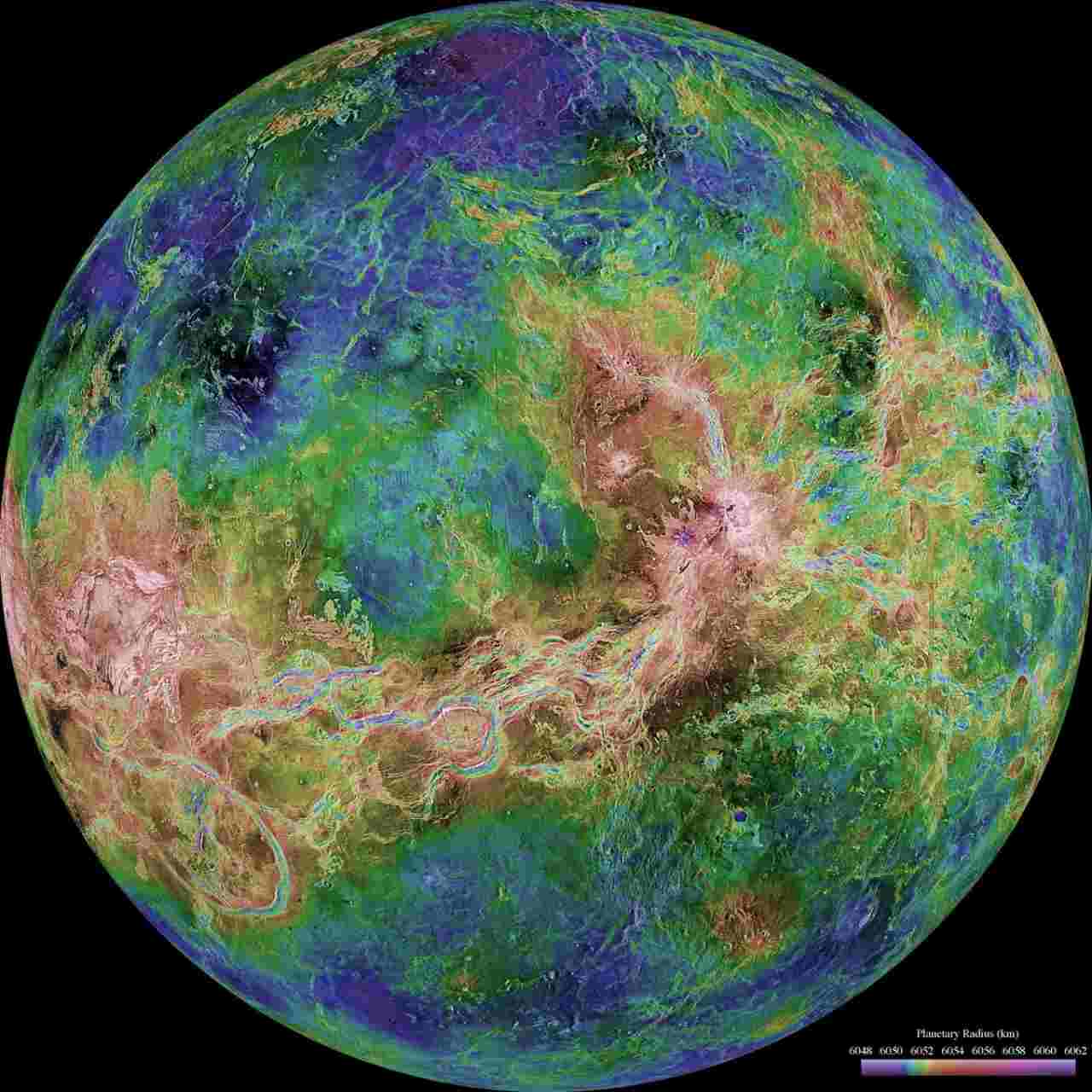
A hemispheric view of Venus – product of over a decade of radar investigations in the 1990-1994 Magellan mission – published on 4 June 1998. Image credit: NASA/JPL/USGS via Reuters
A group of scientists from the Department of Earth Science, Institute of Geophysics, Switzerland and Department of Geology, University of Maryland, USA teamed up to create models of Venus' interior to see what led to the formation of these coronae. To their surprise, the scientists found 37 structures that showed signs of activity within the last few million years.
"For the first time, we were able to pinpoint specific structures and say, ‘Look, this is not an ancient volcano but an active one,’" said the study's co-author Laurent Montesi.
By proving that Venus is geographically active, scientists are looking forward to understanding why two planets so similar in composition and size evolved so differently.
The study was published in the journal [ Nature Geoscience ](http://(https://www.nature.com/articles/s41561-020-0606-1.epdf?sharing_token=4_-VEhNOL_W0bQ8xorVHitRgN0jAjWel9jnR3ZoTv0NJPk3LBkJzNKuzrryJl6HTX7tZ7U3fHEPe0FrLnHRWKtMmqKNGEMwS1s2RwWeU192OUhlOg_yvhbgCcRLVWGOjf8toHU1TsdTVQjhbpWTOhnmkKrVfud12XxrOWesMriqnedLukqhKZdiuJ4IhygSFi7i1c7kiy6GKwBm117hGatPXNDgmeTGonmoIlmRPAvspNcvEvMwnwhUf9wA4OnZ60grlbwSDZNLejtcgTErBaQ%3D%3D&tracking_referrer=www.popsci.com) recently.
Regards