Folks , this sure is a jaw-dropping cavern system - it even contains some of the type of features that Etidorpha described :-
Step inside this massive cave labyrinth hidden under Borneo
Beneath the island’s rainforest, explorers search for new discoveries deep within some of the Earth’s largest, longest, and wildest caves.
At dusk, a swarm of bats disperses to hunt in the rainforest surrounding Deer Cave. One of the planet’s largest underground passages, it holds more than two million bats.
12 Minute Read
By Neil Shea
Photographs by Carsten Peter
This story appears in the March 2019 issue of National Geographic magazine.
Late on a sweltering morning in April, two slim British cavers named Frank and Cookie lowered themselves into a slick, humid pit deep below Borneo’s rainforest.
Climbing down past an ancient heap of bird guano and pushing through a gallery of gleaming pillars the color of old bone, the pair were hoping to make history. They had crawled into Cave of the Winds, deep inside a cave system known as Clearwater, where they would search for a passage to Racer Cave, part of the Racer-Easter system.
Connecting the two would create a “super system,” one of the longest subterranean labyrinths on the planet. As the men wormed down, drilling and hammering bolts into the slick rock to hold their climbing ropes, their odds of success seemed good.
Limestone pinnacles pierce dense vegetation near the center of Malaysia’s Gunung Mulu National Park. Eroded from the thick limestone bedrock over hundreds of thousands of years, these karst features hint at the otherworldly caverns belowground.
Sarawak Chamber, briefly illuminated by dozens of flashbulbs, is the largest cave chamber yet discovered on Earth—more than twice the size of Britain’s Wembley Stadium—and home to thousands of small birds called swiftlets.
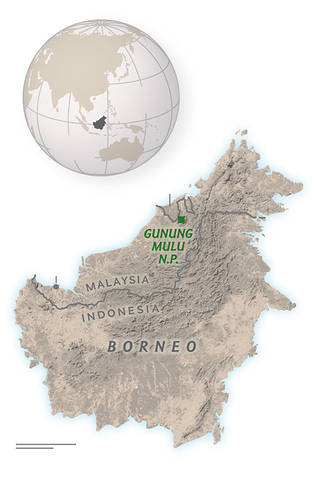
Already they knew Clearwater stretched for 140 miles and that some of the caverns were lined with turbulent rivers, while the Racer-Easter system contained chambers so enormous that a jetliner could fit easily within its walls with plenty of room to spare. In other words, the limestone underlying this region, beneath Malaysia’s Gunung Mulu National Park, is riddled with some of the biggest holes, widest tunnels, and most mind-blowing voids anywhere on Earth.
If you are the kind of explorer who enjoys crawling down into wet, hot darkness in order to find more wet, hot darkness, Borneo is a dreamland, a Disneyland, and a Neverland, all in one.
Now imagine them down there, Frank and Cookie, mud smeared and grinning, on the verge of joining two cave systems into a single, immense whole. Not your thing? Well, for cavers, it’s the thing. And it’s rare that such superlative connections are made. In the often obscure world of underground exploration, which is governed by international bodies with names such as the “Longest, Largest, and Deepest Committee,” such a feat would be a very big deal.
Elsewhere far below the Earth’s surface, in the entrails of Racer Cave, another team was slithering into place. They too carried hammers and a drill, and soon the two teams would begin banging on the cave walls and drilling into the rock, listening for each other, hoping noise would lead them to a connection and a spot in the record books.
Not far above them, I sat in a large gallery, listening for their drills. The gallery was pristine; it had been discovered only days before, and I was one of the first ever to enter it. But where I sat, surrounded by towering stalagmites and colossal mushrooms of stone, the cavern was alive with other sounds. At my elbow, water tinkled into limpid basins, while overhead, thousands of swiftlets—tiny black birds that spend much of their lives in the pitch-black chambers—twittered and clicked and echolocated toward nests made of saliva, moss, and mud.
If Frank and Cookie were making history somewhere below my feet, I wasn’t going to hear it. But that was fine. More than any other sport, caving is about secrets and the things we endure to find them out. Sometimes all you can do is wait to see what the darkness reveals. So I lay back, turned out my light, and listened as the swifts swooped low, coming so close I could feel wingbeats on my cheeks.
“This is a very exciting place. Where else on Earth can you find so much unexplored territory?”
A huge grin lit Andy Eavis’s face. Then the expedition leader frowned.
Left: Waterfalls roughly 400 feet high pour through the roof of Deer Cave after a rainstorm. A few of Gunung Mulu’s caves contain large rivers, which swell into wild torrents during heavy rains.
Right:
Deer Cave is home to several species of bats, which usually fly out in the evenings to hunt.
Thick stands of stalagmites rise from moon-pale banks of sediment in the Drunken Forest—a cave named for formations that tilt at unusual angles. PANORAMA COMPOSED OF FOUR IMAGES
“Well, I suppose there are a few spots,” he said, considering his own question. “Papua New Guinea comes to mind. And of course, there’s the bottom of the sea. But anyway, no. So far as cave exploration is concerned, Borneo is singular. There’s no place like it under the earth.”
Eavis, stout and hale at 70, felt comfortable staking the claim. He has spent more than 50 years exploring some of the world’s most remote and fantastic subterranean systems and has served on nearly every one of his sport’s governing bodies, helping decide how caving records are kept and how titles such as “biggest” and “deepest” are bestowed. Less formally, he’s spent years working to protect caves and ensure they remain open to the cavers who love them. Eavis is, by any measure, an ambassador of the underworld.
It was morning in the rainforest, and Eavis stood on the porch of a research station near park headquarters, preparing to go underground. A sweltering breeze fell through the canopy, silencing the whir of innumerable insects.
Along the walking trails, snails and frogs scurried back into the shadows while birds shrieked and booed at the rising heat. Eavis pulled on black running tights—standard wear for explorers in “hot” caves like those in Borneo, where temperatures can reach 80 degrees F.
Gunung Mulu National Park, located in Malaysia’s Sarawak state on the island of Borneo, is a UNESCO World Heritage site. Below a rolling green carpet of rainforest, its limestone is riddled with some of the planet’s most extensive cave systems.
“Of course, when I got started, we didn’t have kit like this,” Eavis said, waving at the tights. “Or this.” He held up a battered red helmet to which he’d fastened a lamp big as a teacup.
“Back then, we were basically stumbling around in the dark. We had no idea the immensity of the things we’d discovered.”
In 1979, Eavis arrived in Borneo as part of a British expedition designed to study the rainforest and help the recently independent Malaysia understand the newly established Gunung Mulu National Park. Caving was still a relatively young sport, and Eavis and a team of four others were brought on only after expedition leaders realized that there were huge caves among the forest’s many treasures.
Eavis and his friends had honed their skills back home, in Britain, where caves were commonly small and cold. Borneo’s caves, opposite in almost every way, pushed Eavis and his companions into another dimension.
With their first discovery they set their record for size: It was called Deer Cave, or Gua Rusa, and its entrance was so enormous—nearly 500 feet high—that the sun reached deep inside and fresh air followed, creating a strange and wonderful habitat in the seam between daylight and darkness. A mammoth colony of bats clung to the cavern’s roof, while on the floor thick piles of guano teemed with cockroaches, crabs, worms, and hosts of specialized microbes.
Expedition leader Andy Eavis accesses a small algae-covered cave opening. He has been studying and exploring the cave systems below Gunung Mulu National Park since 1979.
The British team found that Deer Cave stretched for nearly two miles, and for a decade afterward it stood as the world’s largest known cave passage. In 1991 a cave discovered in Vietnam, called Hang Son Doong, surpassed it, but the drop in rank did not dull Deer Cave’s allure. Today it’s a major attraction for tourists, who wander its length on a boardwalk and gather at dusk at its mouth, drinks in hand, clapping and sighing as millions of bats stream like smoke into the sky.
Ostentatious, obvious, oversize—Deer Cave hinted at what more awaited underground. Over three months in Mulu, with the help of guides from the nearby Penan and Berawan tribes, the cavers came upon a score of entrances leading deeper into the region’s ancient limestone.
A spelunker appears as a small speck in Deer Cave’s gaping mouth—nearly 500 feet high. Sunlight penetrates deep inside, allowing mosses, ferns, and algae to flourish near the entrance. On the floor, crabs, insects, and bacteria feed on bird and bat guano.
Originally carved by subterranean rivers, Credence cave system was slowly pushed upward by tectonic forces, which lifted it away from water and helped dry it out.
Some of the caves began as obscure cracks in rock faces, covered with brush and branches. These, usually at higher elevations, were older, relatively dry caves that bored through the heart of Mulu’s mountains.
Other caves, at lower elevations, were like giant storm drains—massive holes in the bedrock that channeled rainfall into subterranean rivers. These river caves were younger, formed hundreds of thousands of years ago, lined with beautiful limestone formations, and home to fish, birds, snakes, ghost-white crabs, and a galaxy of insects and spiders.
During their time belowground in 1979, Eavis and his fellow cavers explored some 30 miles of passages—an unprecedented feat. Nearly 40 years later, wearing black tights in the hot syrup of morning, Eavis smiled at the memory.
“There’s no expedition that’s ever explored that much at one time,” he said. “We did most of it standing up, you see.”
Eavis paused, stared down at his tights, and bent at the waist. He picked a leech from his bootlace and flicked it into the jungle.
“Up to that point we were all just simple English cavers,” he said. “Mulu transformed us.”
The 1979 adventure set the stage for exploration in Borneo. Several caving teams have since made the long journey to Mulu, and Eavis himself has led many of them. For his 13th trip, in 2017, he organized a team of 30 cavers, including his son Robert and many Mulu veterans. In late March I reached him by phone in Kuching, a city on Borneo’s west coast, as he traveled north to meet them.
“We will probably find somewhere near 30 miles of new cave passage,” he said confidently. “And nobody ever does that. Except for me, I suppose.”
Two weeks later, when I joined him in Mulu, that faith had been tempered. The expedition was divided into three main teams. Two of them searched for new passages in a remote area of the rainforest while the third, called the “connection team,” pored over maps, looking for spots where different cave systems might be linked.
The towering walls of the Gua Nasib Bagus—Good Luck Cave—gallery dwarf the caving team’s campsite.
So far, Eavis said, the pace of discovery had been slow and the holy grail of connections—the one Frank and Cookie would later probe for—had eluded them. Eavis acknowledged disappointment, but his teams still had found more than seven miles of fresh passage, and more lay ahead.
The morning after my arrival I joined Eavis and a small crew headed for a cave called Gua Nasib Bagus—the Good Luck Cave—which holds the otherworldly Sarawak Chamber. Eavis, with other British explorers, had discovered the cave and the chamber in 1981, by following a river into the side of a mountain.
After climbing, pulling, and crawling upstream for hours, the cavers arrived at a still, calm place where the river vanished into the earth. The men unfurled measuring tapes and began surveying into the gloom, expecting to reach the rear wall soon.
But no wall appeared. So they tried a different tactic, veering sharply, figuring they’d bump into a side wall. They heard swiftlets calling overhead, the river roaring somewhere beneath their feet. Still no wall. Their headlamp beams simply dissolved into the darkness.
After 17 hours of exploring, the men tumbled out of Good Luck Cave, soaked and confused. Either they’d just spent hours walking in circles, or they’d made an astounding find.
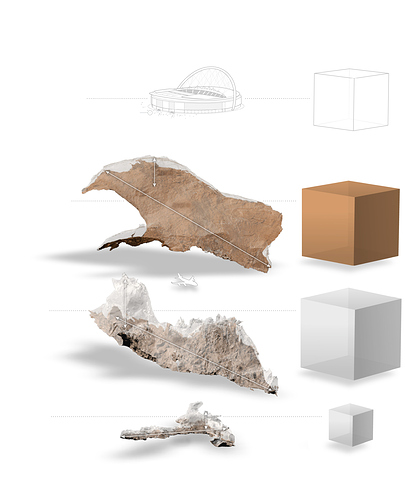
Later teams proved that Sarawak Chamber is the largest known enclosed space on Earth, at 2,000 feet long, 1,400 feet wide, and almost 500 feet tall. It’s more than twice as big as the United Kingdom’s most celebrated sports arena, Wembley Stadium.
Super Caves
Carved from limestone and sandstone, Sarawak Chamber is one of the planet’s largest enclosed areas, natural or manmade.
Equivalent volume
as a cube
141.3 million cubic feet (ft³)
Wembley Stadium
Person
for scale
United Kingdom
Wembley Stadium can hold 90,000 soccer fans. Sarawak is big enough to contain two Wembleys.
280 ft
346.4 million ft³
2,065 ft
Sarawak Chamber
Good Luck Cave
Malaysia
First discovered in 1981, Sarawak Chamber was only recently mapped using laser technology. Scientists continue to search its massive roof for unknown passages.
Boeing 747
for scale
490 ft
374 million ft³
Miao Room
Gebihe Cave
China
Larger than Sarawak Chamber, the Miao Room is Earth’s largest cavern by volume. It holds stalagmites almost as tall as the Statue of Liberty.
2,620 ft
32.8 million ft³
220 ft
The Big Room
Carlsbad Caverns
New Mexico, United States
1,305 ft
The Big Room is the largest cave chamber in the U.S. Tourists can take a one-mile, self-guided walk around its perimeter.
MATTHEW TWOMBLY; BRIAN T. JACOBS, NGM STAFF
SOURCE: ROO WALTERS
OBJECTS ARE TO SCALE. MEASUREMENT SCALES VARY WITH PERSPECTIVE.
As we trekked toward Good Luck through thick rainforest, I asked a caver named Philip Rowsell, known as “Mad Phil,” why an ambitious explorer would return to this storied terrain if so many records had been set here. He told me that caves never reveal everything during a first visit.
“You often find things earlier guys missed. Especially if it’s so frickin’ massive that they’re sort of stunned.”
Sarawak Chamber was so big, Mad Phil explained, that it almost certainly contained new passages—particularly in the roof, where no one had ever searched. Although it’s tempting to think of caves as similar to mine shafts—tunnels that slope relatively straightforwardly down—natural caves are nonlinear and ex-pand and contract according to the movement of rocks, the meandering of water, the work of chaos.
Concepts of “up” and “down” assume subtler meanings underground, where directions can be utterly inverted over a few million years. If someone is exploring the down part of the cave, another caver might try looking up. And up was Mad Phil’s specialty.
His nickname apparently had come from a canoeing stunt during his university years, but Mad Phil was known for climbing cave walls that no one else would even attempt. He and Eavis planned to ascend into the roof of Sarawak Chamber, searching for tunnels that ran through it like hidden passages in the ceiling of a mansion.
Local porters ferry the expedition team’s equipment across an underground river to reach various chambers within the cave system.
Author Neil Shea squeezes through a passage to enter a previously unknown chamber the team had discovered just days before.
Rain fell as we wound through the forest. Gradually it came down harder and faster, the noise drowning all sound and talk. Soon the forest itself blurred, fading in the deluge until all life seemed separated by only the sheerest of membranes.
An hour later we arrived at the mouth of Good Luck Cave, where a river emerged from a tall cleft in a wall of limestone. We waded in and pushed ahead, the clear warm water reaching first to our calves, then swelling over our hips, then shoving into our chests.
The passage widened and grew, opening like a train tunnel above us. Bats and birds commuted through it, occasionally dipping into our headlamp beams, and soon the river became whitewater, blasting through sharp channels of limestone, forcing us onto boulders slick with spray and guano.
The route was so treacherous that in certain places previous cavers had bolted ropes to the walls so they could drag themselves forward against the current.
After a wild and sodden mile, the river disappeared into the earth, and Sarawak Chamber swallowed us into its vastness.
Even when every lamp focused upward, we could see only the dim suggestion of its massive dome. And if we turned our lamps toward the back of the cave, we saw nothing at all. It was easy to imagine Eavis and his friends lost, years before, in the void.
“If you look around, you might find our old boot prints,” Eavis said, laughing. “Stumbling around like blind mice we were.”
The weird thing about caves is that you remember them brightly. Dim in certain corners, but otherwise the walls and rocks and spiders are pretty well illuminated. Photographs only enhance this illusion. What’s true is that except for the instant when a photographer’s flash dumps light through a cavern, most everything is invisible.
With no sunlight to measure time, we marked it with meals, tea, and chocolate bars.
Near the chamber’s entrance, Mad Phil began drilling bolts into the wall, working his way around an overhanging ledge to the roof. The rest of us explored below, pressing forward, sounding the planet’s largest known enclosed space.
Overhead the swifts chattered and bickered and called without rest, occasionally dropping down to land on our chests, where they would sit and allow themselves to be petted.
At “night” we set our bedrolls on flat rock and strung up lines to air out our socks. The chamber was humid and warm, as though the darkness itself were wet, and beyond the edges of camp a constellation of little jewels glinted in the lamplight—the eyes of countless spiders, some as big as my hand.
An expedition team member climbing toward the roof of Deer Cave dangles above a silhouette that looks like Abraham Lincoln. The sharp presidential profile is a natural feature of the limestone and one of the cave system’s many curiosities.
One “day,” with Mad Phil and a young caver named Ben, I explored along the left side of the chamber, searching for another entrance. Sarawak is so large that it contains many distinct precincts, and we climbed through at least half a dozen of them, passing from a pile of loose, muddy boulders into a maze of limestone with walls sharp as the face of a cheese grater, to an eerily quiet niche carpeted with feathers and deep drifts of guano that seemed a place where cave creatures—birds, spiders, crickets, centipedes—went to die.
Beyond that lay a hushed nursery where the cave was so warm, so still, the swifts felt safe laying their eggs on bare ground. We never found another entrance, though surely there was one—the sound of water and swarms of birds told us that. But we’d have to leave it to future cavers.
In the end, Eavis’s team did not rack up more record-setting discoveries. Frank and Cookie—the mud-covered pair, drilling and banging at the bottom of a cave—never connected the Clearwater cave system to its neighbor that seemed so tantalizingly close. But the expedition succeeded in finding and mapping a respectable 14 miles of new passages.
A few weeks after I left Borneo, I spoke with Eavis, who had returned to Britain. He told me he was already planning a return trip to Gunung Mulu National Park to connect the caves himself.
“We were extremely close,” he said.
He assured me it was not the pursuit of records, or the odd celebrity his sport sometimes bestows, that continued to drive him. He thought about the caves every day. His children knew well his stories from under the jungle.
“My guess is that only 50 percent of the passages have been discovered,” he said. “Wouldn’t you just want to know? Mulu is this incredible place, and I want to know what’s down there and see how all the pieces all fit together.”
It was, he said, the labyrinth of a lifetime.
Regards

:focal(775x536:776x537)/https://public-media.si-cdn.com/filer/5c/fa/5cfa252c-9b6c-4f25-963b-cd116c1881f5/oldcowpainting.jpg)

/https://public-media.si-cdn.com/filer/a4/d3/a4d38715-df2c-4efe-81f1-61d3a199ca20/banteng-40000-years-old-dated-panel-.jpg)

